Basic Force and Position Tutorial
This guide provides a simple demonstration of applying forces and visualizing the movement of an Inverse3 cursor. By the end, the Inverse3 will simulate the sensation of being tethered to its starting position with a virtual rubber band, while a spherical GameObject displays the cursor's position.
Introduction
The Getting started Guide introduced the Inverse3 object, its functionality, and the method to generate constant forces. Our objective here is to simulate a rubber band effect on the cursor. A rubber band behaves similarly to a spring, meaning its force is influenced by both the stiffness and the distance between its two endpoints. Thus, we aim to devise a function that, given a position and stiffness, produces a force causing the cursor to resist movement away from the origin.
Scene Setup
Initiate by creating a Haptic Rig (one hand) via the GameObjects > Haply menu.
ForceAndPosition Component
Select the Haptic Origin GameObject and add a new script named ForceAndPosition.cs and populate the ForceAndPosition class with the following code:
[SerializeField]
private Inverse3 inverse3 = null;
[SerializeField, Range(0, 400)]
private float stiffness = 100;
private void OnDeviceStateChanged(object sender, Inverse3EventArgs args)
{
var inverse3 = args.DeviceController;
// Calculate the force.
var force = (inverse3.WorkspaceCenterLocalPosition - inverse3.CursorLocalPosition) * stiffness;
// Apply the force to the cursor.
inverse3.SetCursorLocalForce(force);
}
This segment sets the stiffness at 100 Newtons per meter (N/m), simulating a relatively soft spring.
It also introduces inverse3.WorkspaceCenterLocalPosition, a property that returns the center of the workspace.
This method calculates the force by subtracting the cursor's position from the workspace center, then multiplies the result by the stiffness.
Finally, the force is applied to the cursor using inverse3.SetCursorLocalForce.
Incorporate the OnDeviceStateChanged callbacks in the OnEnable and OnDisable methods, as detailed in the Getting started Guide:
protected void OnEnable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged += OnDeviceStateChanged;
}
protected void OnDisable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged -= OnDeviceStateChanged;
}
Gameplay
Hold the Inverse3 cursor, activate Play Mode, and attempt to maneuver the device. You'll observe that displacing the cursor generates a force. The further the cursor is moved from its starting position, the more pronounced this force becomes.
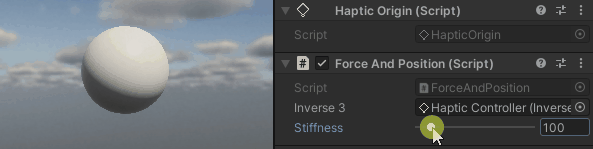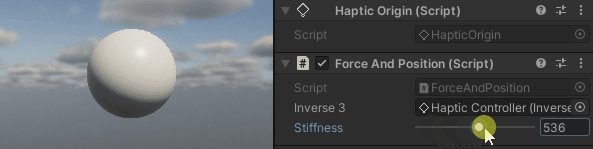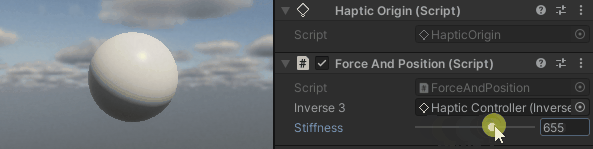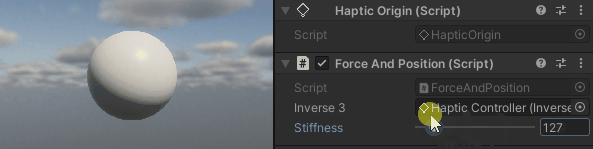
Source files
The final scene and all associated files used by this example can be imported from the Tutorials sample in Unity's package manager.
ForceAndPosition.cs
/*
* Copyright 2024 Haply Robotics Inc. All rights reserved.
*/
using Haply.Inverse.DeviceControllers;
using Haply.Inverse.DeviceData;
using UnityEngine;
namespace Haply.Samples.Tutorials._1_ForceAndPosition
{
/// <summary>
/// Demonstrates the application of force to maintain the cursor at its center position.
/// </summary>
public class ForceAndPosition : MonoBehaviour
{
public Inverse3Controller inverse3;
[Range(0, 400)]
// Stiffness of the force feedback.
public float stiffness = 100;
private void Awake()
{
inverse3 ??= FindObjectOfType<Inverse3Controller>();
}
/// <summary>
/// Subscribes to the DeviceStateChanged event when the component is enabled.
/// </summary>
protected void OnEnable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged += OnDeviceStateChanged;
}
/// <summary>
/// Unsubscribes from the DeviceStateChanged event and reset the force when the component is disabled.
/// </summary>
protected void OnDisable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged -= OnDeviceStateChanged;
inverse3.Release();
}
/// <summary>
/// Event handler that calculates and send the force to the device when the cursor's position changes.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">The Inverse3 data object.</param>
/// <param name="args">The event arguments containing the device data.</param>
private void OnDeviceStateChanged(object sender, Inverse3EventArgs args)
{
var inverse3 = args.DeviceController;
// Calculate the force.
var force = (inverse3.WorkspaceCenterLocalPosition - inverse3.CursorLocalPosition) * stiffness;
// Apply the force to the cursor.
inverse3.SetCursorLocalForce(force);
}
}
}